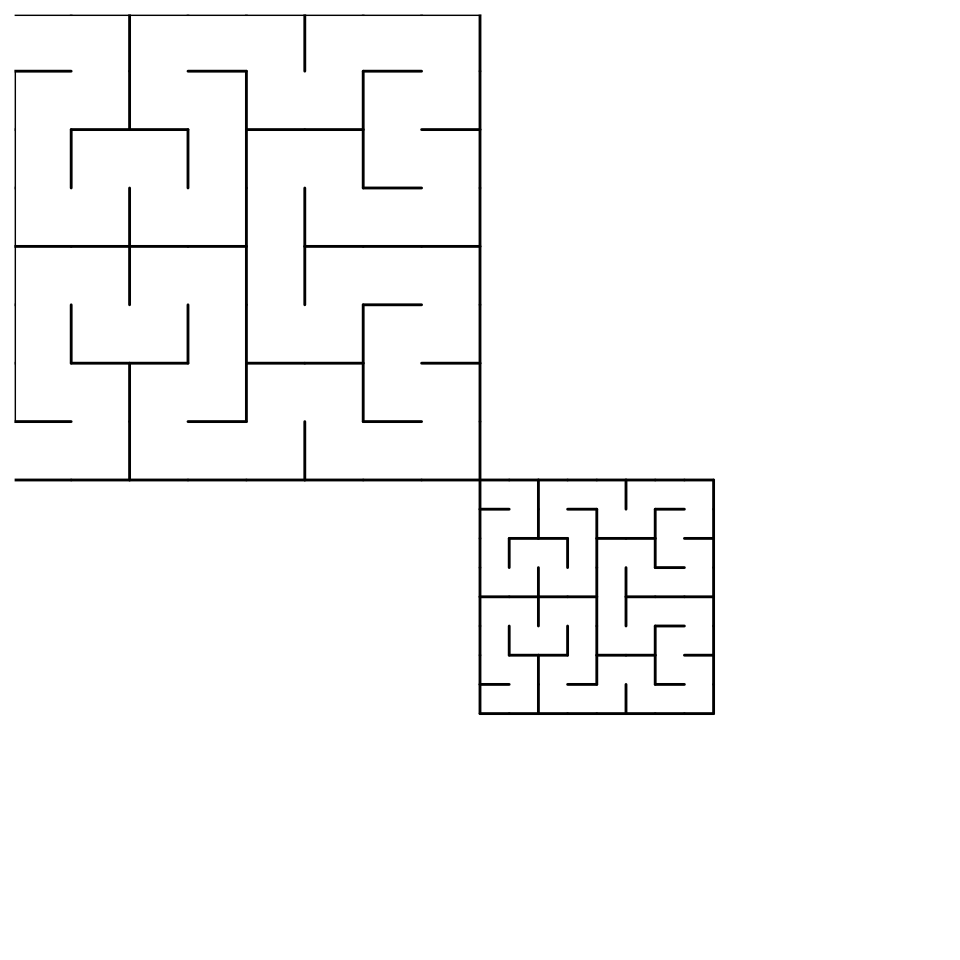
Computes and draws the outline of the Hilbert curve used to map IP data to the Cartesian plane. By superimposing this outline on top of a ggip plot, it guides the eye to regions that are close in IP address space.
Usage
geom_hilbert_outline(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes(). If specified andinherit.aes = TRUE(the default), it is combined with the default mapping at the top level of the plot. You must supplymappingif there is no plot mapping.- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options:
If
NULL, the default, the data is inherited from the plot data as specified in the call toggplot().A
data.frame, or other object, will override the plot data. All objects will be fortified to produce a data frame. Seefortify()for which variables will be created.A
functionwill be called with a single argument, the plot data. The return value must be adata.frame, and will be used as the layer data. Afunctioncan be created from aformula(e.g.~ head(.x, 10)).- ...
Other arguments passed on to
layer(). These are often aesthetics, used to set an aesthetic to a fixed value, likecolour = "red"orsize = 3. They may also be parameters to the paired geom/stat.- na.rm
If
FALSE, the default, missing values are removed with a warning. IfTRUE, missing values are silently removed.- show.legend
logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
NA, the default, includes if any aesthetics are mapped.FALSEnever includes, andTRUEalways includes. It can also be a named logical vector to finely select the aesthetics to display.- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics, rather than combining with them. This is most useful for helper functions that define both data and aesthetics and shouldn't inherit behaviour from the default plot specification, e.g.borders().
Aesthetics
geom_curve_outline() understands the following aesthetics:
ip: Anip_networkcolumn. By default, the entire Hilbert curve is shown.curve_order: How nested is the curve? (default:3).closed: Should the curve outline have closed ends? (default:FALSE).alphacolourlinetypelinewidth
Computed variables
- x, y
The start coordinates for the segment
- xend, yend
The end coordinates for the segment
Examples
p <- ggplot() + coord_ip() + theme_ip_light()
# default shows curve across entire canvas
p + geom_hilbert_outline()
 # only show subnetwork
p + geom_hilbert_outline(ip = ip_network("128.0.0.0/2"))
# only show subnetwork
p + geom_hilbert_outline(ip = ip_network("128.0.0.0/2"))
 # increased nesting
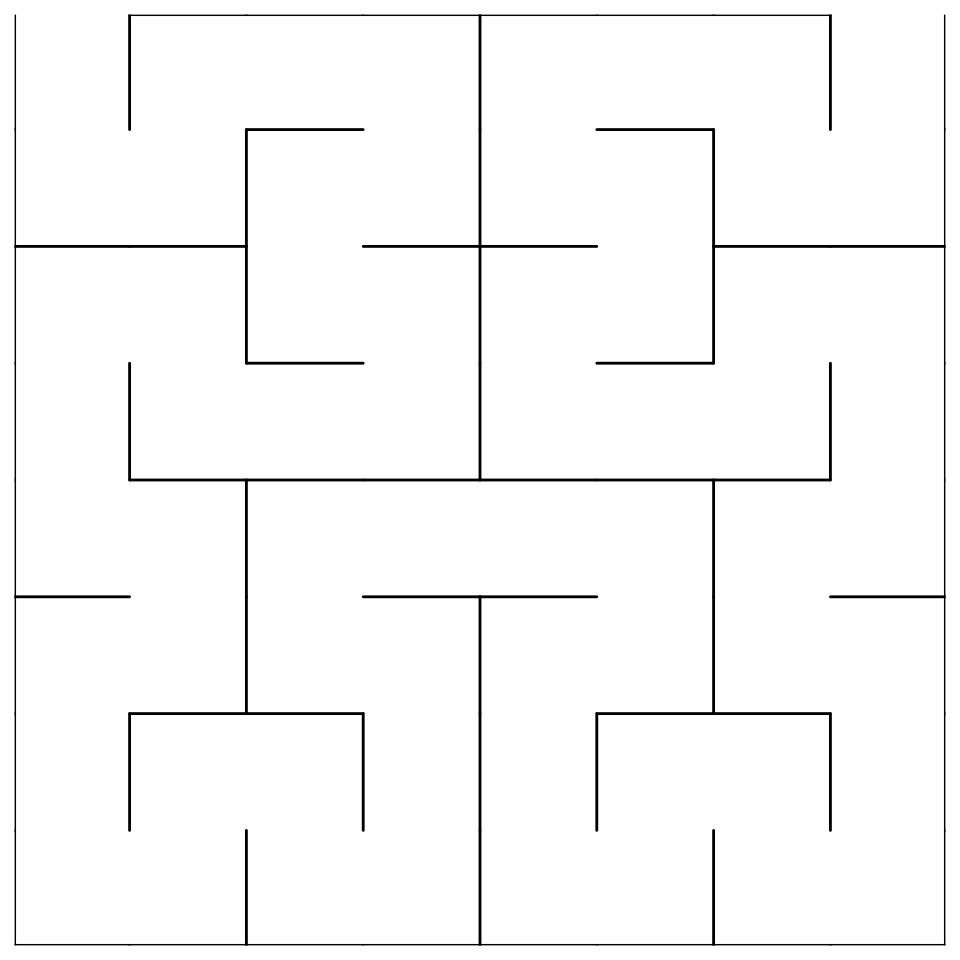
p + geom_hilbert_outline(curve_order = 4)
# increased nesting
p + geom_hilbert_outline(curve_order = 4)
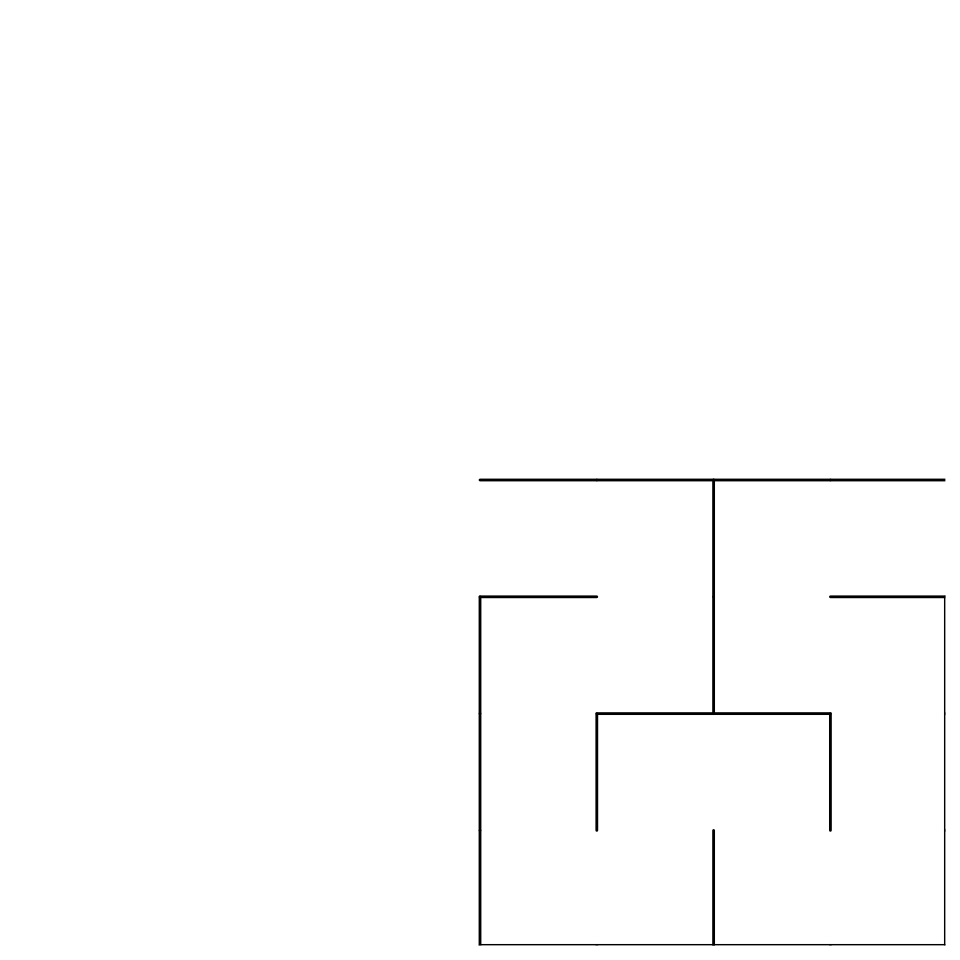
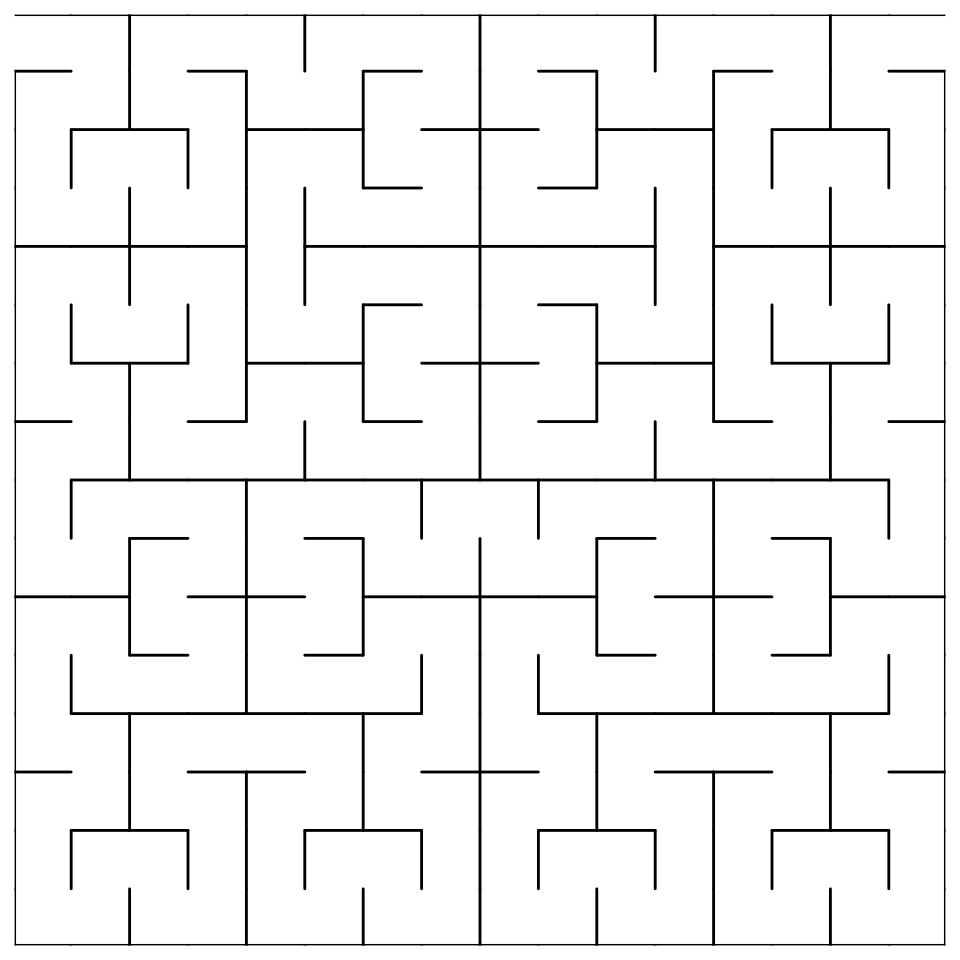 # show multiple networks
df <- data.frame(
ip = ip_network(c("0.0.0.0/2", "128.0.0.0/4")),
curve_order = c(4, 5),
closed = c(FALSE, TRUE)
)
p + geom_hilbert_outline(
aes(ip = ip, curve_order = curve_order, closed = closed),
data = df
)
# show multiple networks
df <- data.frame(
ip = ip_network(c("0.0.0.0/2", "128.0.0.0/4")),
curve_order = c(4, 5),
closed = c(FALSE, TRUE)
)
p + geom_hilbert_outline(
aes(ip = ip, curve_order = curve_order, closed = closed),
data = df
)